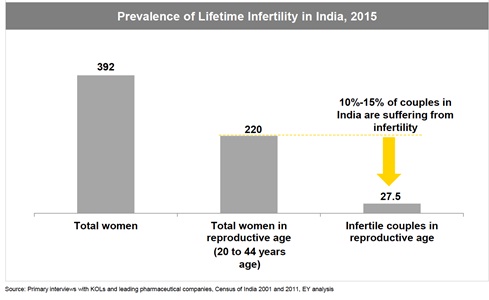
Infertility affects about 15% of the couples globally, amounting to more than 50 million couples. India faces a high burden of infertility, with 22 to 33 million couples in the reproductive age suffering from lifetime infertility. The infertility rate in India has increased significantly over the last several years, which has contributed significantly to a decline in the fertility rate. Childlessness has serious demographic, social, personal and emotional issues. Infertility management would become even more important in near future owing to a large population considering childbearing after thirty years of age, beyond which the fertility sees a significant decline. In addition to this, the modern life-style, lack of exercise, environmental pollutants etc. contribute significantly to the problem of infertility.
 *Adapted from EY July 2015 analysis
*Adapted from EY July 2015 analysis
Understanding genetic causes of male infertility
We are still not able to treat a large number of infertility patients, owing to the lack of understanding of the causes of infertility. Though infertility does not run in families in most of the cases, a susceptible genetic background increase the risk of infertility significantly. We are investigating the genetic causes of infertility, which would help not only in understating the causes but also in designing therapy. Further, understanding of the genetic risk factors could be taken advantage in developing genome-based infertility screening panels for risk prediction early in life. Development of genomics screening panels would help in identification of susceptible individuals early in life, which could be utilized in family planning.
Understanding epigenetic causes of male infertility
In the last one decade, unprecedented role of epigenetic factors in male infertility has been appreciated. It has been found that a number of environmental factors may raise infertility risk by affecting epigenetic modulations. Aberrations in the epigenetic marks that are required to control the process of spermatogenesis may alter gene expression profile, resulting in poor sperm count or motility. Epigenetic changes act as soft modulators of genome activity to regulate spermatogenesis according to the environmental changes, thus placing another line of control over the genetic constituents. We are investigating the epigenetic changes that drive loss of sperm count and increase the risk of infertility. This would identify the soft DNA marks that could be modulated (in future) for infertility treatment.
Treatment of male infertility
The lack of understanding of the causes of infertility translates into poor or inadequate therapeutic options for infertility management. A number of therapies including general anti-oxidants, hormones and empirical treatments are employed; however, there is no treatment specifically and scientifically validated for the treatment of male infertility. The problem of infertility is multi-pronged and it requires a therapy with multiple and varied effects. Plant products are known to have multiple adaptogenic effects by providing essential ingredients, nutrients, hormone regulators and anti-oxidants. We are interested in identification of plant products based treatment of male infertility. We have specific leads in this area, which are being studied in further details for use in male infertility treatment.
View More..