We have developed new approaches for introducing cell-selectivity in AMPs by modulating heptad repeat sequences of either naturally occurring AMPs or designer peptides without compromising their antibacterial properties. In order to introduce stability in the AMPs, we are incorporating unnatural amino acids at various positions of a naturally occurring AMP or a designer antimicrobial peptide. We are also trying to introduce self-assembling property in these AMPs so that they can adopt nano-structures which seem to possess significant stability against proteolytic enzymes.
Anti-endotoxin peptides are considered as potential lead molecules for the development of anti-sepsis agents since gram negative bacterial membrane component, LPS, is a key stimulator host pro-inflammatory responses. Recently, we have been able to design cell-selective anti-endotoxin peptides by incorporating very selective and minimum amino acid substitution in the peptide sequence. Further, we intend to work on the peptides derived from proteins that are associated with LPS-recognition in the host or down-stream signaling events for the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines to investigate their biological property particularly their influence on the LPS-induced pro-inflammatory cytokine production in macrophages/monocytes.
Considering the demand of antimicrobial and anti-endotoxin peptides, successful design of peptides with desired biological profiles will be of significant importance and of potential pharmacological application.
Besides, working on antimicrobial/anti-endotoxin peptides, we are trying to identify protein-fragments with anti-diabetic and/or anti-obesity effects. Recently we characterized one such fragment from human adipokine, adiponectin. We also work on identification and characterization of protein-fragments with bone anabolic effects. We have designed new variants of self-assembling peptide, KLD-12 to introduce antimicrobial attribute in it so that it can fight against secondary infection which is a common occurrence during the external application of such tissue-engineering biomaterial.
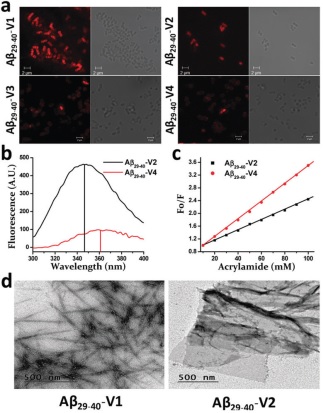
(a) Confocal microscopy for the detection of localization of Rho-labeled Ab29-40-variants onto E. coli. For each variant treatment (concentration, 15 mM), the
fluorescence and DIC images of E. coli are shown. (b) Fluorescence spectra of Ab29-40-V2 and Ab29-40-V4 in the presence
of PC/PG lipid vesicles (200 mM) in PBS. (c) Stern–Volmer plots for acrylamide quenching of tryptophan fluorescence of
Ab29-40-V2 and Ab29-40-V4 in PC/PG lipid vesicles. (d) TEM images indicating the nanostructure forming property of
Ab29-40-V1 and Ab29-40-V2 (Ref: Chem Commun (Camb). 2017;53(97):13079-13082.)
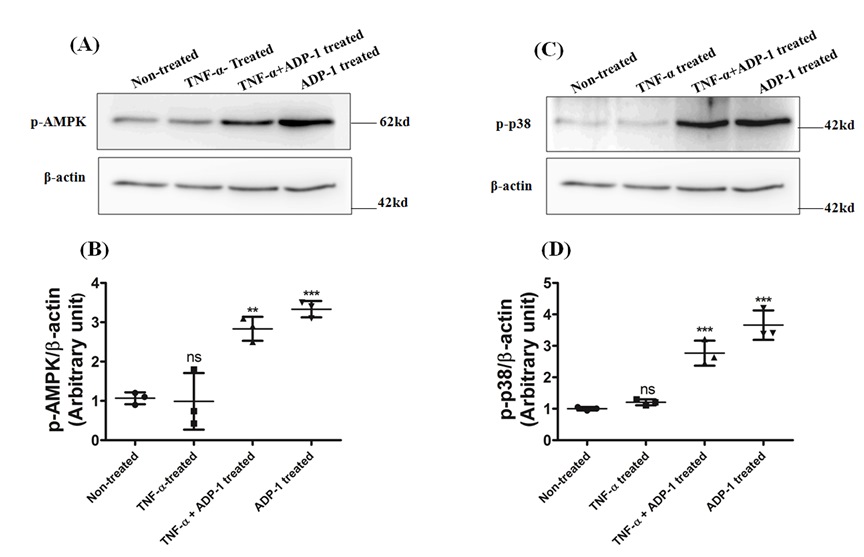
Restoration of phosphorylations of AMPK and p-38-MAPK in TNF-α treated (10 μg/ml for 24 h) L-6 myotubes by adiponectin-derived peptide,
ADP-1 as studied by western blot analyses.
Non-treated cells were taken as basal control, followed by only TNF-α Treated cells, TNF-α with ADP-1 (14.3 μg/ml) treated and lastly only ADP-1 treated (14.3 μg/ml for
3 h). (B). Densitometric quantification of phospho- AMPK relative to β-actin. (C) Non-treated cells were taken as basal control, followed by only TNF-α Treated
cells, TNF-α with ADP-1 (14.3 μg/ml) treated and lastly only ADP-1 treated (14.3 μg/ml for 3 h). (D) Densitometric quantification of phospho- p38 MAPK relative
to β-actin. Results shown are mean ± SD of three independent experiments significance p < 0.001, relative to control (Ref: J. Biol. Chem. (2018) 293(35),
13509–13523).