Shakil Ahmed, Ph.D.
Principal Scientist, Pharmacology
Highlights of our recent research work
Understanding the role of S. pombe Wat1/Pop3, a mammalian Lst8 ortholog in TORC pathway and cellular homeostasis
DNA double strand breaks (DSBs) are critical lesions that can lead to genomic instability.
In response to DNA damage, Chk1, a serine/threonine kinase arrest cell cycle progression to prevent
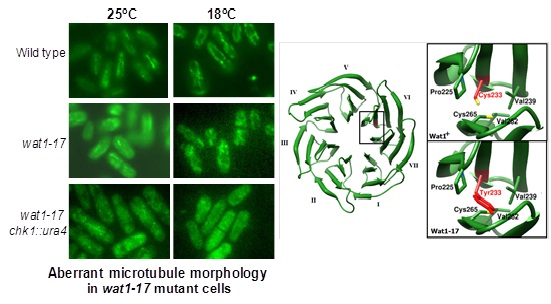
damaged cells interring into the mitosis. A marginal decrease in the level of α tubulin protein level
was observed in wat1-17 mutants. Interestingly the protein level of α-tubulin was reduced in the chk1Δ
wat1-17 double mutant at 18oC with defective microtubule structure. Based on the molecular modeling
studies, we hypothesize that the substitution of the bulky Tyr residue at Cys233 position in wat1-17
mutant results in conformational changes. This in turn can affect its interactions with other
interacting partners and perturb the overall functions of the Wat1 protein.
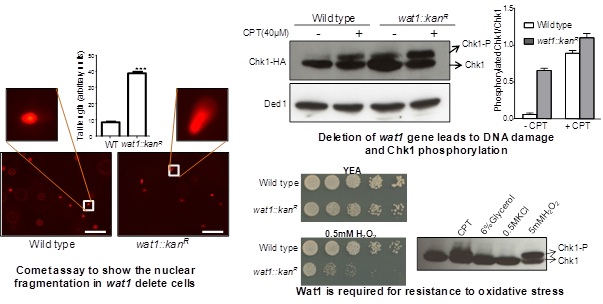
The disruption of wat1, a WD repeat containing protein leads to the phosphorylation of Chk1 along with the high level of nuclear fragmentation. Further, studies have revealed the role of Wat1 during the oxidative stress response with elevated level of reactive oxygen species (ROS) in wat1 null mutant. In mammalian and yeast cells ROS are produced from various sources, with a key source being the mitochondrial electron transport chain. Mammalian Lst8, a Wat1 ortholog interacts with the kinase domain of mTOR and stabilizes its interaction with Raptor that regulates cell growth via mTOR-S6K1 signalling pathway. Earlier we have shown that the Wat1 protein undergoes hyper-phosphorylation at S116 position and interacts with the C-terminal region of Tor1 that also contain kinase domain. The interaction of Gad8 (a substrate for Tor1 kinase) with the TOR complex is dependent on Wat1 phosphorylation as well as its interaction with Tor1 and hence the regulation of downstream pathway of TOR signalling is achieved. Currently our lab is involved in exploring the role of Wat1 protein and its phosphorylation in regulating the TORC1 and TORC2 signalling pathway which will provide a better understanding of these pathways which can be further utilized to develop the Wat1/pop3 as a potential target for anti cancer therapeutics.
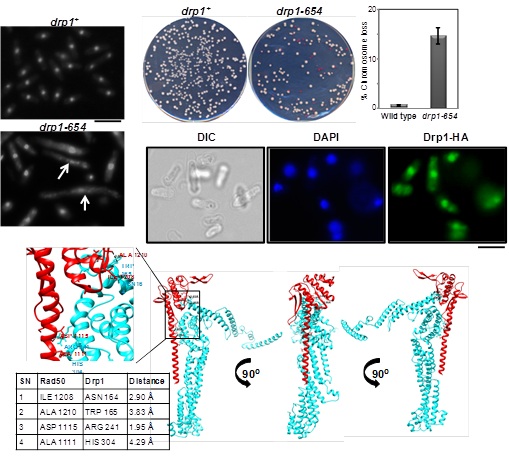
The essential N-terminal region of Drp1 interacts with Rad50 protein and is required for recovery from DNA damage and genome integrity in fission yeast
The defects in DNA repair and replication fork progression results in DNA double-strand breaks that can lead to genomic instability and cancer. Earlier we have shown that the fission yeast Drp1, a Rint1/Tip1 family protein is required for the recovery from DNA damage and interacts with Rad50 protein. Further, we have analyzed the functional and structural aspects of fission yeast Drp1 protein and observed that the N-terminus region of Drp1 is indispensable for its growth and survival. The C-terminus truncations of drp1 (drp1C1Δ, drp1C2Δ) and previously reported drp1M218I mutant cells exhibit temperature sensitive phenotype. These truncations also exhibit hypersensitivity against DNA damaging agents and have an elevated level of Rad52-YFP foci indicating its role in the DNA repair pathway. The essential N-terminus region of Drp1 interacts with the C-terminus region of Rad50 and might be involved in influencing the MRN/X function during the DNA damage repair process. Small-angle X-ray (SAXS) analysis revealed three-domain like shapes in Drp1 protein while the C-terminus region of Rad50 exhibit unusual bulges. Furthermore, using protein-protein docking studies we have identified the amino acid residues present at the C-terminus region of Rad50 that are involved in the interaction with the residues present at the N-terminal region of Drp1.