Global phenotype level alteration studies:
(1) Chronic hyperinsulinemia exposure reduces browning of brown adipocyte:
We here with for the first time report that hyperinsulinemia-induced insulin resistance in brown
adipocyte is also accompanied with reduced insulin sensitivity and brown adipocyte characteristics.
CI treatment decreased expression of brown adipocyte-specific markers (such as PRDM16, PGC1α, and UCP1)
and mitochondrial content as well as activity. CI-treated brown adipocytes showed drastic decrease in
oxygen consumption rate (OCR) and spare respiratory capacity. Morphological study indicates increased
accumulation of lipid droplets in CI-treated brown adipocytes. We have further validated these findings
in vivo in C57BL/6 mice implanted with mini-osmotic insulin pump for 8weeks. CI treatment in mice leads
to increased body weight gain, fat mass and impaired glucose intolerance with reduced energy
expenditure and insulin sensitivity. CI-treated mice showed decreased BAT characteristics and
function. [ Ref: J Endocrinol. 2016 Sep;230(3):275-90. doi: 10.1530/JOE-16-0099.]
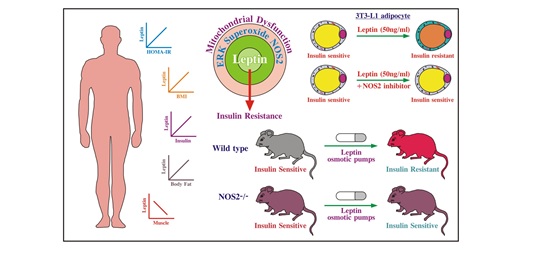
(2) Chronic hyperleptinemia induces insulin signaling disruption in adipocyte-Role of NOS2:
Chronic leptin (50ng/ml) treatment in 3T3-L1 adipocytes decreased insulin-induced phosphorylation of nodal
insulin signaling proteins along with reduced glucose uptake. Metabolic flux studies indicated
mitochondrial dysfunction and reduced oxygen consumption rate. Leptin treatment also increased both
cellular and mitochondrial superoxide levels concomitant to increased expression of nitric oxide
synthase-2 (NOS2). Further, pharmacological depletion of NOS2 reversed leptin mediated effects on
insulin signaling. In-vivo implantation of leptin osmotic pumps in C57BL/6 mice also decreased insulin
responsiveness. Interestingly, these effects were lacking in NOS2 knockout strain. In conclusion, our
studies put forward a potential link between leptin and adipocyte insulin responsiveness in an NOS2
dependent manner [Free Radic Biol Med. 2017 Jul 22;112:93-108. doi: 10.1016/
j.freeradbiomed.2017.07.016].
Tissue level insulin resistance associated studies:
(3) Temporal immuno-metabolic profiling of the adipose tissue in HFD induced obesity and insulin
resistance:
The purpose of the study the roles of immune cell subsets, their interrelationship, and chronological events leading
to progression of obesity-associated insulin resistance (IR). In the temporal HFD settings, mice showed progressive
glucose intolerance, insulin resistance, and adipose tissue senescence. Flow cytometry analysis of the stromal
vascular fraction (SVF) from eWAT revealed T-cell subsets as early-phase components and pro-inflammatory
macrophages, as well as mast cells as the later phase components during obesity progression. macrophage
depletion by Clodronate and mast stabilization by Disodium chromo glycage attenuated obesity, adipose tissue
fibrosis, and improved whole-body glucose homeostasis. In addition, mast cell stabilization also attenuated
senescence (p53 and X-gal staining) in eWAT, signifying the role of mast cells over macrophages during obesity.
[Ref: Int J Obes (Lond) 2019 Jun;43(6):1281-1294. doi: 10.1038/s41366-018-0228-5.]
(4) Role of brown adipose tissue in modulating adipose tissue inflammation and inflammation in
HFD fed mice:
Purpose of this study was to investigate the immunometabolic role of brown adipose tissue (BAT) in the obesity. We
performed both BAT transplantation as well as extirpation experiments in the mouse model of high-fat diet
(HFD)-induced obesity. BAT transplantation reversed HFD-induced increase in body weight gain and insulin resistance
without altering diet intake. BAT transplantation attenuated the obesity-associated adipose tissue
inflammation-decreased pro-inflammatory M1-macrophages, cytotoxic CD8a T-cells and restored anti-inflammatory
regulatory T-cells (Tregs) in the eWAT. BAT transplantation also improved endogenous BAT activity by elevating
protein expression of browning markers (UCP-1, PRDM16 and PGC1α) in it. In addition, BAT transplantation promoted
the eWAT expression of various genes involved in fatty acid oxidation (such as Elvol3 and Tfam,). In contrast,
extirpation of the interscapular BAT exacerbated HFD-induced obesity, insulin resistance and adipose tissue
inflammation (by increasing M1 macrophages, CD8a T-cell and decreasing Tregs in eWAT). Taken together, our results
suggested an important role of BAT in combating obesity-associated metabolic complications [Ref: Eur J Pharmacol.
2019 Feb 26. pii: S0014-2999(19)30149-9. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2019.02.044].
Novel protein target identification:
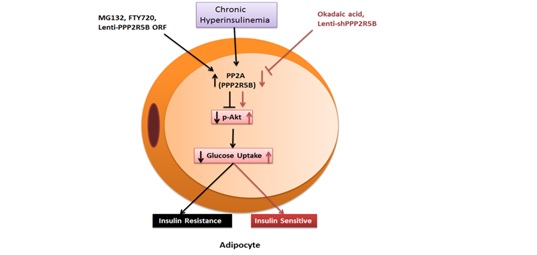
(5) PPP2R5B-
This is regulatory subunit of the phosphatase PP2A which contributes to insulin resistance development. There is
increased level of expression of PPP2R5B in insulin resistance adipocyte as well as HFD fed mice white adipose
tissue. Overexpression, suppression and chemical intervention studies indicated role of PPP2R5B in insulin
resistance development as a negative regulator of AKT phosphorylation [Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2016 Dec 5;437:97-107.
doi: 10.1016/j.mce. 2016.08.016.].
Novel regulatory microRNA targets:
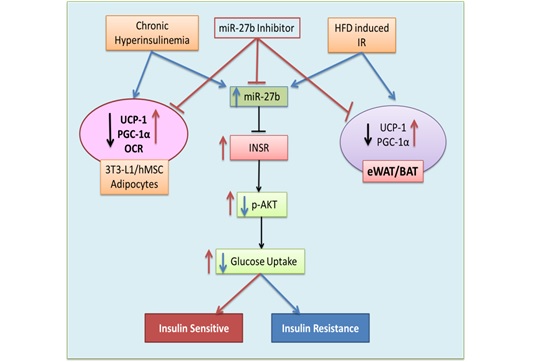
(6) miR27b-
This mi-RNA is part of cluster miR-23b-27b-24-1 that was found to be significantly upregulated in
differential mi-RNA expression studies in insulin sensitive and insulin resistant 3T3-L1 adipocyte
(mouse). This miRNA was earlier not reported in literature and picked up in our screen due to our
physiological model system. Lentiviral mediated overexpression in vitro and in vivo studies proved
its contribution in insulin resistance development. Our systematic modulation studies identified that
it directly regulated expression of insulin receptor by targeting its 3’ UTR [Ref: J Mol Med (Berl).
2018 Apr;96(3-4):315-331. doi: 10.1007/s00109-018-1623-z] .
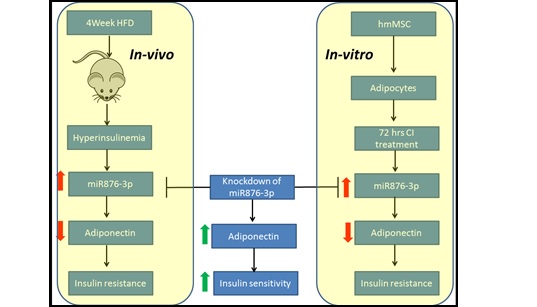
(7) miR876-3p:
Using hMSC derived adipocyte exposed to hyperinsulinemia micromilieu, we performed differential miRNA profiling and
identified miR876-3P as candidate microRNA that is altered in insulin resistance. Our results highlight that
miR-876-3p regulate glucose homeostasis and its dysregulation leads to IR. We found that miR-876-3p level is
a critical determinant of adiponectin expression by virtue of its target within adiponectin 3′UTR. Regulatory
effect of miR-876-3p impacts crosstalk between adiponectin and insulin signaling. lentiviral-mediated inhibition
of miR-876-3p expression ameliorated CI and high-fat diet (HFD)-induced IR in adipocytes differentiated from hMS
C and C57BL/6 mice, respectively[Ref: J Endocrinol. 2018 Jul 2. pii: JOE-17-0387. doi: 10.1530/JOE-17-0387] .
Novel non-coding Circular RNA targets:
(8) Mitochondrial Circ-RNA:
Our sequencing studies also identified novel circ-RNAs when insulin resistant adipocyte were profiled against
insulin sensitive adipocyte. One of the miRNA was of high interest because it was of mitochondrial origin. None of
circ-RNA of mitochondrial origin has been reported yet in case of insulin resistance. We have employed
overexpression and suppression studies for overall phenotype analysis. We have progressed to identify couple of
its possible RNA protein binding targets. Currently we are working on elucidation signaling alterations and
molecular mechanistic profiling of this MT-CircRNA.
Drug Discovery studies and contributions:
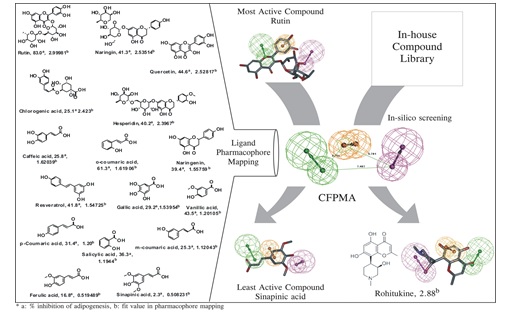
(9) Common feature pharmacophore model of anti-adipogenic compounds- A virtual in silico screening
tool:
Exploiting all literature information, we curated set of anti-adipogenic compounds and their relative
anti-dyslipidemic capabilities. Using this library of compounds, we developed CFPMA model which we used for
screening of natural product compound libraries. We identified several unknown/not reported natural products
capable of inhibiting adipogenesis which is also one of the therapeutic strategies to reduce obesity and
dyslipidemia [Ref: J Lipid Res. 2014 Mar 19;55(6):1019-1032] .
Natural Molecules and natural molecule inspired synthetic molecules:
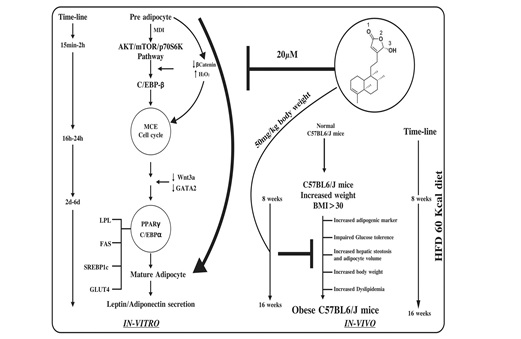
(10) Rohitukin-Antiobesitic and anti dyslipidemic:
: Rohitukine downregulated expression of PPARγ, CCAAT/enhancer binding protein α, adipocyte protein 2 (aP2), FAS,
and glucose transporter 4. It also suppressed mRNA expression of LPL, sterol-regulatory element binding protein
(SREBP) 1c, FAS, and aP2, the downstream targets of PPARγ. Rohitukine arrests cells in S phase during mitotic
clonal expansion. Rohitukine increased hepatic expression of liver X receptor α and decreased expression of SREBP-2
and associated targets. Rohitukine decreased hepatic and gonadal lipid accumulation and ameliorated dyslipidemia
significantly. Rohitukine thus exhibited in vitro antiadipogenic activity and also exhibited in vivo
antidyslipidemic activity [Ref: J Lipid Res. 2014 Mar 19;55(6):1019-1032].
(11) CDRI 4655- Clerodane di-terpene- Antihypertriglyceridemic and antiobesitic:
The distant structural similarity between compound 1 and lovastatin (polyketide class of compound) prompted us to
investigate effects of diterpene compound 1 on adipogenesis and thereby obesity. it reduced expression levels of
PPARγ, C/EBPα and GLUT4 during differentiation. Diterpene compound reduced MDI induced-Akt/mTOR phosphorylation
and expression of cell cycle proteins, and thereby halted mitotic clonal expansion. It also exhibited
anti-adipogenic activity in murine mesenchymal cell-line C3H10T1/2 and human mesenchymal stem cell models of
adipogenic differentiation. When compound 1 was administered along with HFD, for another 8 weeks in 2 month HFD
fed overweight mice, it attenuated weight gain and epididymal fat accumulation. It improved body glucose tolerance,
reduced HFD induced increase in total cholesterol and leptin/adiponectin ratio. Because of its distinct
anti-hyper-triglyceridemic property, which is important problem in Indian population, this molecule has been
selected for IND enabling studies by CSIR-FTT taskforce (Ref: Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2015 Jan 5;399:373-85.
doi: 10.1016/j.mce.2014.09.024].
(12) Curcumin 3-4-dichlorophynyl pyrazone (CDPP):
Curcumin exhibit weak anti adipogenic activity due to its bioavailability issue. We selected this pharmacophore to
increase curcumin bioavailability while retaining biological property. CDPP was found to be a potent inhibitor of
adipogenesis in-vitro. It blocked mitotic clonal expansion by causing cell cycle arrest. CDPP showed marked
improvement in gastrointestinal stability and bioavailability in-vivo as compared to curcumin (in 100 folds).
Administration of CDPP (100mg/kg) significantly improved HFD induced dyslipidemic profile in hamsters and activated
reverse cholesterol transport machinery. CDPP is potent pro-drug of curcumin [Ref: Metabolism. 2017 Aug;73:109-124.
doi: 10.1016/j.metabol.2017.05.005]
(13) Ecliptal:
a natural compound isolated from the herb Eclipta alba. This molecule inhibited adipogenesis by modulating WNT-Beta
catenine pathway. Ecliptal treatment augmented mitochondrial biogenesis as well as function as estimated by
expression of PGC1α, UCP-1, mitochondrial complexes and estimation of oxygen consumption rate. Ecliptal also
reduced LPS-induced inflammation and tunicamycin induced ER stress. Further, Ecliptal enhanced insulin
sensitivity by increasing AKT phosphorylation, inhibiting PKCα/βII phosphorylation and reducing leptin/adiponectin
ratio. Finally, Ecliptal administration in Syrian golden hamsters was shown to have potent anti-dyslipidemic
effects [Ref: Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2018 Jan 1;338:134-147. doi: 10.1016/j.taap.2017.11.016.].
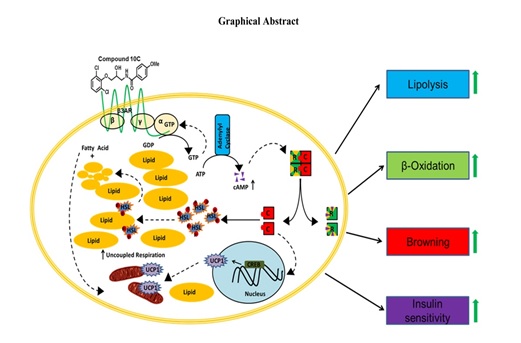
(14) Aegeline Inspired Synthesis of Novel β3-AR Agonist
Improves insulin sensitivity in Vitro and in Vivo Models of Insulin Resistance. This is novel
N-acyl-1-amino-3-arylopropanol synthetic mimics of aegeline which we named compound 10C. This compound 10C was
found to be the most active and specific β3-AR agonist with EC50 value of 447 nM. The compound 10C activated β3AR
pathway, induced lipolysis, fatty acid oxidation and increased oxygen consumption rate (OCR) in human adipocytes.
Compound 10C induced expression of brown adipocytes specific markers and reverted chronic insulin induced insulin
resistance in white adipocytes. The compound 10C also improved insulin sensitivity and glucose tolerance in 8
week HFD fed C57BL6 mice
[Ref: Metabolism. 2018 Mar 7. pii: S0026-0495(18)30067-2. doi: 10.1016/j.metabol.2018.03.001] .
Synthetic molecules:
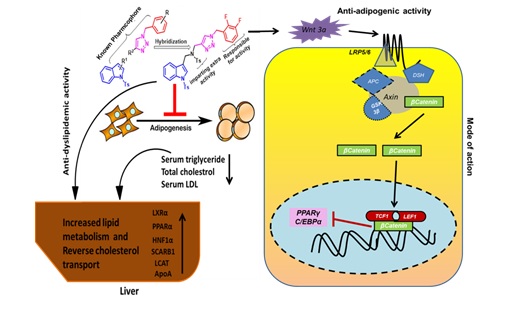
(15) Novel indole and triazole based hybrid molecules :
These molecule exhibit potent anti-adipogenic and antidyslipidemic activity by activating Wnt3a/β-catenin pathway.
These molecule has been proved to be anti-adipogenic in vitro and anti-dyslipidemic in vivo by activating reverse
cholesterol transport proteins like PPAR alpha and LXR- alpha.
Flavopiridol:
This is synthetic analogue of the rohitukine and found to be highly potent anti-adipogenic inhibitor as well as anti-obesitic in nature. Molecular activities are similar to that of rohitukine as explained earlier.
S013-1051:
This molecule is highly interesting molecule as it acts as insulin sensitizer by activating PI3K-AKT pathway. This molecule also has indirect AMPK activation capabilities similar to metformin. In around 4 in vitro models of insulin resistance and 6 in vivo models of insulin resistance/type-2 diabetes/obesity models molecule has exhibited highly significant activity. We are currently working on this molecule development further.
Regulatory pharmacology studies carried out GLP framework:
This is important regulatory pharmacological activity conducted by Team-CSIR-CDRI.We are important task force member in seeking accreditation of NGCMA-GLP accreditation to CSIR-CDRI by laying down Standard operating procedures, study designs, data reporting format and data archival formats.