Leishmaniasis
Synthesis, Biological Evaluation, Structure−Activity Relationship and Mechanism of Action Studies of Quinoline-metronidazole Derivatives against Experimental Visceral Leishmaniasis
To identify novel chemical scaffolds for the development of antileishmanial agents, a series of quinoline-metronidazole was synthesized and tested
against murine model of visceral leishmaniasis. Among all synthesized derivatives, 15b and 15i showed promising antileishmanial efficacy against both
extracellular promastigote (IC50 9.54 µM and 5.42 µM respectively) and intracellular amastigote (IC50 9.81 µM and 3.75 µM respectively) form of
L. donovani with
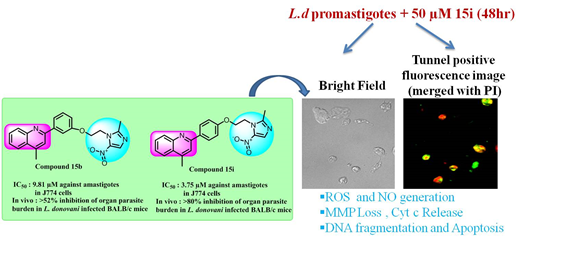
negligible cytotoxicity towards host (J774 macrophages, Vero cells). However compound 15i showed better in vivo efficacy and
effectively eliminated spleen and liver parasite burden (>80 %) in BALB/c mice model of VL. Mechanistic studies revealed that 15i triggers oxidative
stress, induces bioenergetic collapse and apoptosis of the parasite by depleting ATP production and loss in mitochondrial membrane potential.
Structure−activity analyses and pharmacokinetic studies revealed 15i as a promising antileishmanial lead and suggests quinoline-metronidazole series
as a suitable platform for future development of antileishmanial agents. (J Med Chem. (2019) 62(11):5655-5671)
Differential induction of SOCS isoforms by Leishmania donovani impairs macrophage- T cell crosstalk and host defense
Immune evasion strategies adopted by Leishmania donovani involve the exploitation of SOCS proteins that are well-known negative regulators of the
JAK/STAT pathway. However, the cellular mechanism underpinning the induction of SOCS isoforms and their role in breaching the multilevel regulatory
circuit connecting the innate and adaptive arms of immunity are still ambiguous during experimental visceral leishmaniasis. Using bone marrow
macrophages (BMMфs) and CD 4+ T cells, we observed that L. donovani preferentially upregulates SOCS1 and SOCS3 expression in macrophages and T
cells respectively, while SOCS1 level remains consistently high in BMMфs, SOCS3 expression is pronounced and long-lasting in T cells. Consequently,
this inhibits STAT1 mediated IL-12 induction in macrophages & STAT4 mediated IFN-γ synthesis in T cells. Mechanistically, PI3K/Akt-mediated SRF
activation promotes nuclear translocation and binding of Egr2 to SOCS1 promoter for its early induction in infected BMMфs. Additionally, L. donovani
activates
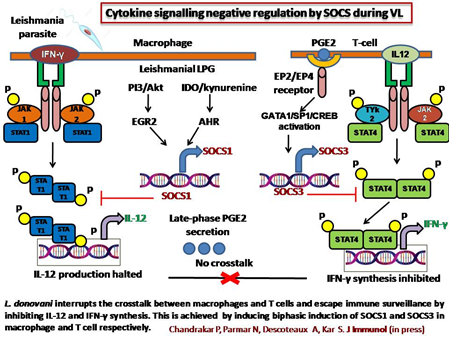
IDO/kynurenine/AHR signaling in BMMфs in order to maintain prolonged SOCS1 expression. Later, prostaglandin E2, secreted from infected
BMMфs induces cAMP-PKA pathway by binding to the EP2/EP4 receptor of CD 4+ T cells, leading to SP1, CREB and GATA1 activation and SOCS3 expression.
SiRNA-mediated silencing of SOCS1 and SOCS3 in macrophage and T cells respectively restored IL-12 and IFN-γ cytokine levels and BMMфs-T cell
interaction. Vivo morpholino-mediated silencing of SOCS1 and SOCS3 resulted in protective cytokine responses, thereby reducing organ parasite burden
significantly in L. donovani-infected Balb/c mice. Collectively, our results imply that L. donovani orchestrates different SOCS isoforms to impair
macrophage-T cell crosstalk and preserve its own niche. (J Immunol, 2019, PMID: 31882519)
Effect of overexpression of of LdMAPK1 on Leishmania proteome:
Mitogen-activated protein kinases (MAPKs) are well-known mediators of signal transduction of eukaryotes, regulating important processes,
like proliferation, differentiation, stress response, and apoptosis. In Leishmania, MAPK1 plays various roles in regulating the critical
cellular activities like parasite survival, infectivity and drug resistance. Earlier, we have shown that LdMAPK1 modulates antimony
susceptibility by downregulating P-glycoprotein (P-gp) efflux pump and plays a vital role in the post-translational modification and
possibly the regulation of heat shock proteins. With an aim to identify LdMAPK1 modulated phosphoproteins by comparative phosphoproteomics
analysis of wild type (Dd8+/+), LdMAPK1 over-expressing (Dd8++/++) and LdMAPK1 single deletion (Dd8+/-) mutant parasites, iTRAQ labeled
quantitative analysis was carried out. Biological triplicates were run on orbitrap fusion and the protein search was performed against
L. donovani database down loaded from Uniprot using Proteome Discoverer 2.2 software. Comparatively, iTRAQ labeling based quantitative
analysis identified 420, 512, 320 phosphopeptides for 210, 255 and 142 phosphoproteins in biological triplicates of wild type (Dd8+/+),
LdMAPK1 over-expressing (Dd8++/++) and single deletion (Dd8+/-) mutant parasites respectively. Out of these, only 8 phosphoproteins
namely, acetyl-coenzyme A synthetase, heat shock protein 83-1, serine/threonine-protein phosphatase, elongation factor 1-alpha, nucleolar
protein, and 3 uncharacterized protein exhibited ˃1.5 fold upregulation in LdMAPK1 overexpressing parasites while 7 proteins,
(eukaryotic translation initiation factor 5a, eukaryotic release factor-3, glyceraldehydes-3-phosphate dehydrogenase, enolase, heat
shock protein 70 and two ribonucleoside diphosphate reductase small chain proteins showed >1.6 fold down-regulation. However, except one
(eukaryotic translation initiation factor 5a), none of the either up or down regulated proteins, in overexpressing parasites, exhibited
differential expression in single deletion mutant parasites. The study suggests that LdMAPK1 over-expression modulates the expression
levels of phosphoproteins related to diverse pathways mostly related to metabolism, signal transduction, translation and molecular
chaperones.
Functional Characterization of TCP1γ of L. donovani
As drug target: T-complex polypeptide-1 (TCP1), a group II chaperonin class of protein (HSP60 family) is involved in intracellular assembly and
folding of various proteins in eukaryotes. In Leishmania, only the TCP1 subunit has been cloned and characterized from our lab. It forms
homo-oligomeric complex and exhibited chaperonin activities. In the present study, we evaluated the essentiality of LdTCP1γ gene using both molecular
and chemical validation strategies. Gene replacement studies indicate that LdTCP1γ is essential for parasite survival as efforts to generate null
mutant failed and single-allele replacement mutants exhibited retarded growth and decreased infectivity in mouse macrophages compared to wild-type
parasites. Modulation of LdTCP1γ expression in promastigotes also modulated cell cycle progression. Suramin, initially developed as a treatment for
human African sleeping sickness, exhibited significant inhibition of LdTCP1γ refolding activity and multiplication of amastigotes with low toxicity
to mammalian cells. The interaction of suramin with LdTCP1γ was observed both by isothermal titration calorimetry and computational molecular
docking studies. The study suggests that LdTCP1γ is an essential gene, hence a potential drug target. It also provides a framework for the
development of a new class of drugs.
As immunogen: Treatment of VL is associated with the generation of Th1 type of cellular response and antigens that are involved in Th1 stimulation are
considered as a suitable vaccine candidate. Interestingly, the recombinant protein, LdTCP1γ was found to be potent immunogenic in nature as it exhibited
strong Th1 type response. It exhibited strong LTT response along with significant NO and ROS production in cure hamsters as compared to untreated infected
controls. The study suggested that LdTCPγ is a promising molecule which has to be further evaluated for its prophylactic efficacy.
Characterization of leishmanial dipeptidylcarboxypeptidase as a potential vaccine molecule against visceral leishmaniasis
Peptidase from parasite origin are becoming important as vaccine candidate, among them cell surface metallopeptidase and lysosomal cysteine peptidase
have shown immunoprophylactic activity. From our lab, dipeptidylcarboxypeptidase (LdDCP) a zinc metallopeptidase has been reported as a potent drug
target. In the present study, LdDCP was evaluated for its immunogenicity in cured hamster by XTT, NO and RO production. The study suggested that
LdDCP has potential of developing as vaccine candidate against VL infection
Characterization of RNA Editing Ligase 1 (REL1) of Leishmania donovani as drug target
RNA editing is a unique posttranscriptional modification of mitochondrial mRNAs that is shared in all trypanosomatid pathogens. Modification of specific editing sites, dictated by complementary guide RNAs (gRNAs), constitutes essential steps to ensure the production of translatable mRNAs that encode essential components of the mitochondrial oxidative phosphorylation system which is indispensible for survival of Leishmania parasite inside host. One of the important components of RNA editing is RNA editing ligase 1 (REL1). We aim to characterize RNA editing pathway, particularly the enzyme, REL1 of L. donovani (LdREL1) in the context of parasite survival and infectivity.
Peptidase from parasite origin are becoming important as vaccine candidate, among them cell surface metallopeptidase and lysosomal cysteine peptidase
have shown immunoprophylactic activity. From our lab, dipeptidylcarboxypeptidase (LdDCP) a zinc metallopeptidase has been reported as a potent drug
target. In the present study, LdDCP was evaluated for its immunogenicity in cured hamster by XTT, NO and RO production. The study suggested that LdDCP
has potential of developing as vaccine candidate against VL infection.
LdREL1 has been expressed and purified. We now started preparing over-expression and knock-out construct of LdREL1 to establish its function in
Leishmania parasites. A 0.8 kb flanking sequence upstream (5′F) and 0.725 kB flanking sequence downstream (3′F) of LdREL1 were PCR-amplified from
L. donovani g-DNA, cloned in pCR-2.1-TOPO TA vector and then sub-cloned in pX63NEO and pX63HYG vectors in between HindIII and SalI as well as SmaI
and BglII sites to generate 5′F-pX63HYG-3′F and 5′F-pX63NEO-3′F constructs respectively. Both of these circular constructs were then digested with
HindIII and BglII to generate linear constructs for transfection in Leishmania parasites. Transfection of knock-out construct will be started to
generate LdRELl deleted parasites to see the effect of this knockout in parasite survival and infection
To prepare over-expression construct, LdREL1 ORF was PCR amplified from a pCR- 2.1-TOPOTA-LdREL1 construct using primers with restriction sites
HindIII and BamHI and cloned into Leishmania expression vector pLp-NEO2 in between HindIII and BamHI sites. Clone pLp-NEO2-LdSir2 (ORF in the right
orientation) has been transfected into Leishmania parasites by electroporation. Transfectants were selected and maintained in the presence of 40 mg/mL
G418 and further selected in 80 mg/mL G418. Taking these LdREL1 knockout and over-expression parasites, the role of REL1 in RNA editing, oxidative
phosphorylation, parasite survival and infectivity will be explored in future.
Development of Leishmania vaccine
Previously identified 6 Th1 stimulatory proteins are being evaluated for their prophylactic as well as therapeutic efficacy against visceral
leishmaniasis (VL). In continuation, we have now developed a chimeric protein by fusing eldolase and triosephosphate isomerase (TPI) and evaluated
its therapeutic efficacy against experimental VL. When compared to the individual proteins, the fusion product has shown significantly increased
therapeutic efficacy. The suppression of infection was more than 75% when used with BCG as an immune modulator. The immunological parameters such
as DTH response, lympho-proliferation as well as cytokine responses for both Th1 type (IFN-γ, TNF-α and IL-12) and Th2 type (IL4 and TGF-β) in the
splenic tissue samples as well as in the sera samples indicated inclination towards Th1 response. Development of chimeras of aldolase-enolase and
aldolase-TPI is underway.